Step 1 - Understanding the relation between volume percent and parcial pressure
The parcial pressure of a gas in a mixture can be obtained by the following expression:
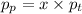
In the equation above, pp represents the parcial pressure and pt the total pressure. x is the molar fraction, which can be defined as:
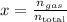
I.e., is the quociente between the number of moles of the gas you want to calculate the parcial pressure of and the total number of moles.
Since, for a gas, the number of mols is proportional to the volume, the molar fraction is equal the volume percent:
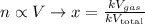
K is a constant of proportionallity. It doens't matter its value, since it will be cancelled. We obtain thus:
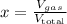
I.e., the molar fraction is exactly equal the volume percentage.
Step 2 - Using the relation between parcial pressure and volume percentage to solve the exercise
Since, as we saw, the molar fraction x is exactly equal to the volume percentage, we can substitute it by the volume percentage in the formula for the parcial pressure:
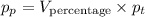
From the exercise, we know that:
![\begin{gathered} V_{\text{percentage}}=27.1\text{ \% = 0.271} \\ \\ p_t=759\operatorname{mm}Hg_{} \end{gathered}]()
Substituting these values on the equation we obtain the parcial pressure of Neon:
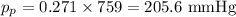
The parcial pressure of Neon is thus 205.6 mmHg.