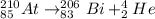Answer: The following equation represents the alpha decay of At-210:
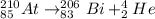
Explanation:
The question requires us to write down the chemical equation for the alpha decay of At-210.
An alpha decay process occurs when an unstable nucleus releases a particle containing 2 protons and 2 neutrons (an alpha particle, also known as He-4). A generic equation for this nuclear process can be written as:
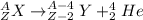
Note that, as the mass number (A) of an atom is given by the sum of its protons and neutrons, an alpha decay results in an element with mass number = A - 4. Also, as the atomic number (Z) corresponds to the number of protons of an atom, after an alpha decay, this atomic number will be Z - 2.
For At-210, the mass number after the alpha decay will be 210 - 4 = 206, and its atomic number will be 85 - 2 = 83. Since the nucleus formed will have tomic number 83, it is a bismuth (Bi) atom (Bi-206).
We can write the following equation to represent this alpha decay: