We have a combustion reaction, in which hexane (C6H14) reacts with oxygen gas to form water and CO2. The balanced equation for this reaction is:
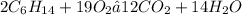
Now, we are given the mass of the reactants and asked to find the yield of water produced. To find this unknown we will follow the following steps:
1. We find the moles of reactants. To do this we divide the given mass by the molar mass of the compound.
Molar mass C6H14: 86.18g/mol
Molar mass O2:31.9988g/mol
2. We find out which is the limit reactant. We will divide the moles found by the respective stoichiometric coefficient. The one that is in smaller proportion will be the limit reactant. Remember that the limiting reactant is the one that produces the least amount of products.
3. We find the theoretical moles of water that will be produced from the limiting reactant. For this, we take into account the ratio and the stoichiometric coefficients of the reaction.
4. We find the theoretical grams of water, and multiply the moles of water by the Molar mass of water.
Molar mass of water: 18.015g/mol
5. We find the percent yield of water with the following equation:
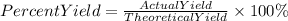
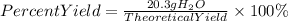
Let's proceed with the calculations
1. Moles of reactants
Oxygen gas
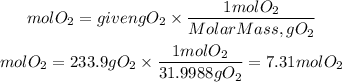
Hexane
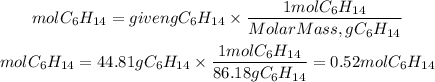
2. Limiting reactant
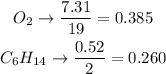
We see that the smallest ratio is for hexane, so hexane is the limiting reactant.
3. Moles of water
The ratio H2O to C6H14 is 14/2. So, the moles of water will be:
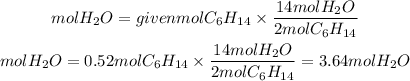
4. Grams of water
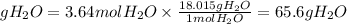
5. Percent yield of water
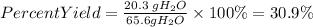
Answer: The percent yield of water is 30.9%