Interval notation is a way of writing the subsets of the real number line.
There are 2 types of brackets used to represent two types of intervals on the number line.
A closed interval is one that includes its endpoints. Closed brackets, [ ], are used to write out the intervals. For example, the interval 0 ≤ x ≤ 3 is represented as:
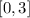
An open interval is one that does not include its endpoints. Open brackets, ( ), are used in this case. For example, the interval 0 < x < 3 is represented as:
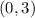
The interval in the question is given to be:
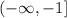
This means that the interval contains all real numbers less than or equal to 1:

ANSWER: The answer is "less than or equal to".