Part A:
Given the function
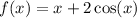
, the absolute maximum or minimum occurs when
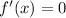
.

Using the second derivative test,
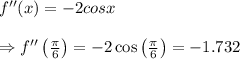
Since the second derivative gives a negative number, the given function has a maximum point at
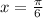
.
And the maximum point is given by:
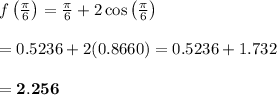
i.e.
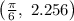
Part B:
Given the function
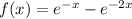
, the absolute maximum or minimum occurs when
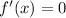
.
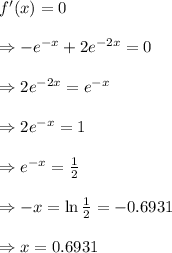
Using the second derivative test,
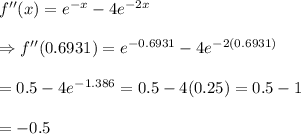
Since the second derivative gives a negative number, the given function has a maximum point at
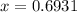
.
And the maximum point is given by:
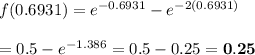
i.e. (0.693, 0.25)