We have the oxidation reaction of magnesium. We are given the balanced equation for the reaction so we can continue with the calculations.
We will first calculate the theoretical yield, the theoretical yield corresponds to the mass of magnesium oxide that would be produced if all the available magnesium reacts since in this case we are told that magnesium is the limiting reactant.
To calculate this mass we do the following calculations:
1. We must first convert the mass of magnesium to moles using the molar mass of magnesium. The molar mass of Mg is 24.305g/mol.
2. We will also take into account the stoichiometric ratio. The equation tells us that 2 moles of magnesium produce 2 moles of magnesium oxide. So, the ratio of MgO to Mg is 2/2.
3. We convert the moles of MgO found in grams. We must multiply the moles by the molar mass of MgO. The molar mass of MgO is 40.3044g/mol.
So, the grams of MgO produced theoretically will be:
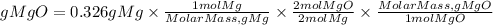
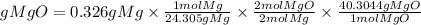
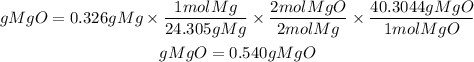
The theoretical yield will be equal to 0.540 grams of MgO.
To find the percent yield we must apply the following equation:
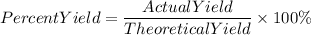
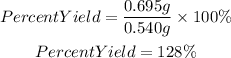
We have an inconsistency in the percent yield value, it is mayor than 100%. This is because the current mass of MgO is greater than the theoretical one, this is not possible in reality.