In order to determine the coefficient of linear expansion of this metal, we can use the following formula:
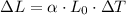
Where DeltaL is the change in length, alpha is the coefficient, L0 is the initial length and DeltaT is the change in temperature.
So, for DeltaL = 0.002 m, L0 = 3.521 m and DeltaT = 88°C , we have:
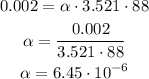
Therefore the coefficient is 6.45 * 10^-6 °C^-1.