The data shows the number of books per shelf in the library.
The variable of the study is X: the number of books on each shelf.
The data is arranged in a frequency table, in the first column you see the number of books per column and on the second column, you see the absolute frequency.
So, for example, in the first row, we see that 3 shelves have 12 books, and in the second row we have the information that three shelves have 40 books, and so on...
To calculate the expected value of a sample shown on a frequency table you have to use the following formula:
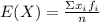
Where
xi represents each possible observation of the variable X
fi represents the absolute frequency of each observation
n represents the sample size
To determine the sample size, which is the total number of shelves, you have to add all observed frequencies:
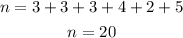
Next is to calculate the expected value, you have to multiply each observation by its corresponding frequency and add them together, then divide the result by 20:
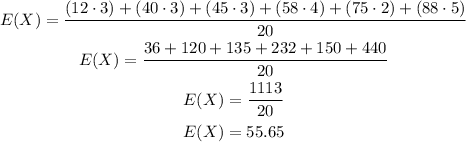
The expected value is E(X)=55.65 books