Given the following equation,
a. (2x + 5)(x + 1)
b. (x - 2)(x + 2)
Let's transform them into an equivalent standard form using the distributive property:
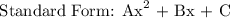
We get,
a. (2x + 5)(x + 1)
(2x + 5)(x + 1) = (2x)(x) + (2x)(1) + (5)(x) + (5)(1)
= 2x² + 2x + 5x + 5
(2x + 5)(x + 1) = 2x² + 7x + 5
b. (x - 2)(x + 2)
(x - 2)(x + 2) = (x)(x) + (x)(2) + (-2)(x) + (-2)(2)
= x² + 2x - 2x - 4
(x - 2)(x + 2) = x² - 4