Answer:
1.80 g (grams) of glucose.
Step-by-step explanation:
First, we dissolve 20.0 g of glucose in a volume of water of 100 mL (0.1 L), so let's calculate the concentration of glucose in g/L, like this:
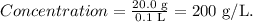
Now, we take 45 mL (0.045 L) of this solution that contains a concentration of glucose of 200 g/L to create a new solution with 0.500 L.
From this new solution, we have to find the mass of glucose if we took 100 mL (0.1 L) of this solution, so we have to use the following equation:

Where C is concentration, V is volume, and subindex 1 and 2 indicate the initial solution, which in this case, is C1 = 200 g/L, V1 = 0.045 L, and the final solution with unknown concentration (C2) and a volume of V2 = 0.500 L.
Let's solve for C2 and replace the given data to obtain the new concentration (final concentration) of the new solution of 0.500 L, like this:
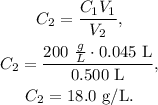
The final concentration of glucose in 0.500 L would be 18.0 g/L.
The next and final step is to calculate the total mass using the volume that we took from the 0.500 L solution, which is 100.0 mL (0.1 L). To do this, we have to do a dimensional analysis to obtain the answer in units of grams, so the calculation will look like this:
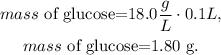
The answer would be that we have 1.80 g (grams) of glucose in 100 mL from the 0.500 L solution.