Answer:
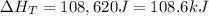
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since we can evidence that the ice is firstly undergoing a melting process at constant 0.0 °C, whose associated enthalpy change is:
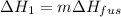
Next, the formed liquid water undergoes a heating from 0.0 °C to 22°C, to the associated enthalpy change is:
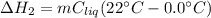
Thus, the total enthalpy change, or heat added to the system turns out:
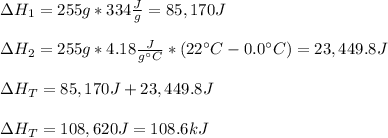
Best regards!