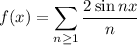The full range is
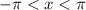
(length

), so the half range is
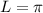
. The half range sine series would then be given by
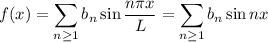
where
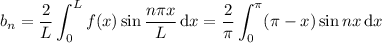
Essentially, this is the same as finding the Fourier series for the function
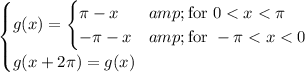
Integrating by parts yields
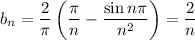
So the half range sine series for this function is simply