Given data:
* The velocity of the car is 13.6 m/s.
* The distance traveled by the car before coming to rest is 0.321 m.
* The mass of the child is 21.2 kg.
* The final velocity of the car is 0 m/s.
Solution:
By the kinematics equation, the velocity of the car in terms of the acceleration and the distance traveled is,
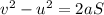
where v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity, S is the distance tarveled, and a is the acceleration,
Substituting the known values,
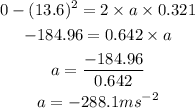
Here, the negative sign is representing the decrease in the value of velocity with time.
By the Newton's second law, the force acting on the child in terms of the mass and acceleration is,
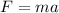
where m is the mass of the child,
Substituting the known values,
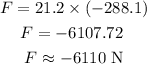
Thus, the magnitude of force acting on the child in three significant figures is 6110 N.