First, find the LCM of the denominators (x-2) and 3. It is 3(x-2).
Multiply both sides of the equation by the LCM to cancel out all the denominators. Then, solve for x.
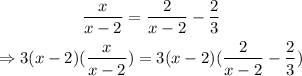
Expand the parenthesis on the right member of the equation:
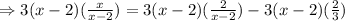
Cancel out the factors that appear on the denominator in each term:
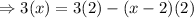
Expand the parenthesis on the right member of the equation:

Expand all the parentheses and solve for x:
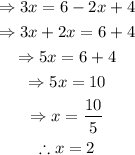
Notice that the expression x-2 appears in the denominator. Nevertheless, since the value of x that would make the equation true is 2, then the expression x-2 is equal to 0. On the other hand, the denominator cannot be equal to 0 because division over 0 is not defined.
Therefore, this equation has no solution (the solution set is the empty set).