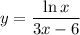
Differentiate both sides with respect to

:
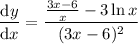
When
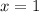
, you have
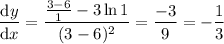
For part (b), we now assume that

and
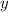
are functions of an independent variable, which we'll call
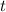
(for time). Now differentiating both sides with respect to
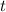
, we have
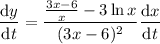
where the chain rule is used on the right side. We're told that
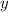
is decreasing at a constant rate of 0.1 units/second, which translates to
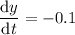
. So when
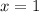
, you have
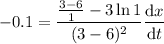
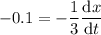
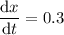
where the unit is again units/second.