The current induce at the point can be given as,
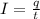
Plug in the known values,
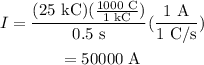
The magnetic field produced at the point P is given as,
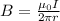
Substituting values,
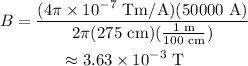
Therefore, the current induced in the wire is 50000 A, the magnetic field acting on the point is
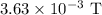
which acts in the anticlockwise direction as the current moves in the upward direction.