Considering a gene with two alleles "A" (dominant) and "a" (recessive). The allelic frequency of one of the alleles of the gene is the frequency of the said allele is the population of interest. To calculate this frequency you have to consider individuals that are homozygous for the allele and the heterozygous individuals.
There are three types of genotypes for the given gene in the population of plants:
AA (dominant homozygous) these individuals carry two identical dominant alleles "A"
Aa (heterozygous) these individuals carry one copy of each allele "A" and "a"
aa (recessive homozygous) these individuals carry two identical recessive alleles "a"
To calculate the frequency of the dominant allele "A" in the population of plants, you have to count the number of alleles "A" observed in the population and divide it by the total number of alleles in the population:
- Dominant homozygous individuals have two copies of the allele "A", so the number of alleles is equal to twice the number of dominant homozygous individuals.
- Heterozygous individuals have only one copy of the allele "A", so the number of alleles is equal to the number of heterozygous individuals in the considered population.
-Recessive homozygous individuals carry no copies of the allele "A".
-The individuals of the population have two alleles for the given gene, so the total number of alleles of the population is equal to twice the number of individuals of the population.
Using the following formula you can calculate the frequency of A:
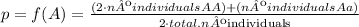
nº individuals AA= 10
nº individuals Aa= 10
Total nº individuals= 50
Calculate the frequency
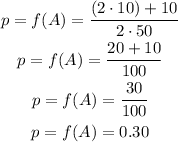
The allelic frequency of the dominant allele "A" is p=0.30