Answer
The new volume = 0.503 L or 503 mL
Step-by-step explanation
Given:
Initial volume, V₁ = 480 mL = (480/1000) = 0.480 L
Initial temperature, T₁ = 45.0°C = (45 + 273 K) = 318 K
Final temperature, T₂ = 60.0°C = (60 + 273 K) = 333 K
What to find:
The new volume, V₂ when the temperature increases to 60.0°C.
Step-by-step solution:
Since the pressure is constant, the new volume, V₂ can be calculated using Charle's law formula.
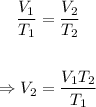
Plugging the values of the given parameters into the formula, we have
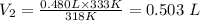
The new volume, V₂ when the temperature increased to 60.0°C = 0.503 L or (0.503 x 1000 mL) = 503 mL