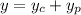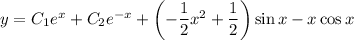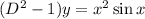
First consider the homogeneous part,
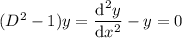
which has characteristic equation
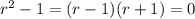
This has roots
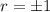
, so the characteristic solution is
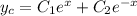
For the nonhomogeneous part, consider a solution of the form
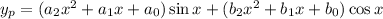
which has second derivative

Substituting into the ODE gives
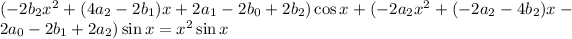
Matching up coefficients gives the system
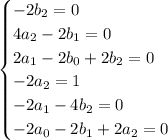
which has solutions
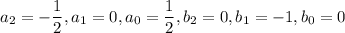
So the particular solution is
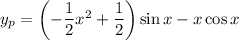
Therefore the general solution is