To calculate this, we will need to assume the gas behaves as an ideal gas.
So, we can use the Ideal Gas Law:
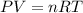
Where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, is the absolut temperature and R is the gas law constant.
Since we have carbon dioxide, CO₂, we need to calculate its molar mass to convert the mass to number of moles:
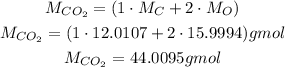
So, the number of moles is:
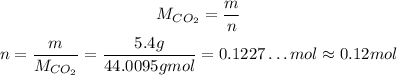
Also, we need to convert the temperature to absolute temperature, so we can convert it to K by adding 273.15 to the degree celcius temperature:
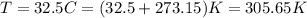
Now, we need to use the constant R that has the unit we want. We have K for temperature, mol for number of moles and L for volume. Is we want the pressure in kPa, we need to use the R constant with units L*kPa/(K*mol), which have the value:
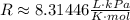
So, solving the equation for P and substituting the values, we have:
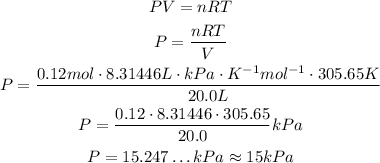
So, the pressure is approximately 15 kPa.