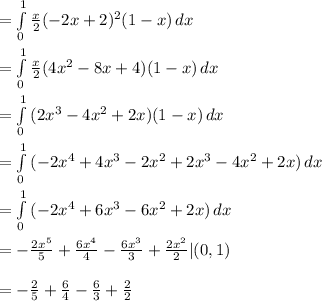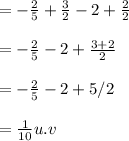Hi, We can to calculate the vectors.
And the determinant will be the plan Z
Let A = (0,03), B =(0,2,0) , C = (1,0,0) and D = (0,0,0)
Then,
AB = B - A
Replacing the points:
AB = (0,2,0) - (0,0,3)
AB = (0i, 2j , -3k)
----------------------------
Already the vector AC = C -A
That's is,
AC = (1,0,0) - (0,0,3)
AC = (1i, 0j, -3k)
Then,
The plan =
![\left[\begin{array}{ccc}x&y&z\\0&2&-3\\1&0&-3\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/hxgthn11wto72cxfutni61mxd1kcrhh3yf.png)
Solving it, we will have:
Plan: -6x -3y -2z + d = 0
Replacinng any point to find the value of d
Example the point A =(0,0,3)
-6(0) -3(0) -2(3) + d = 0
-6+d = 0
d = 6
Then, The us equation will stay of form following :
-6x -3y -2z +6 = 0
or
6x + 3y +2z -6 = 0
Isolating 2z:
2z = 6 -6x - 3y
Dividing both the sides od equation by 2
z = 3 - 3x - 3y/2
Then,
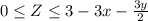
Now, Let's find the
domain in xy
|y
| (0,2)
|\
| \
| \
| \ (1,0)
------------------------- x
b = Cut in y
then b will be = 2
As y = ax + b
y = ax + 2
We have the point = (1,0)
Replace in the equation
0 = a(1) + 2
0 = a + 2
Isolate a
a = -2
Then us stay:
y = -2x + 2
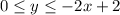
-------------------------------------
With ,
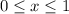
----------------------------------------
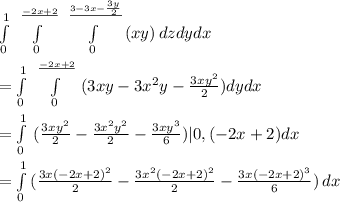
Now putting 3x/2(-2x+2)² as commu factor
![\\ = \int\limits^1_0 {((3x(-2x+2)^2)/(2) - (3x^2(-2x+2)^2)/(2) - (3x(-2x+2)^3)/(6) )} \, dx \\ \\ = \int\limits^1_0 { (3x)/(2)(-2x+2)^2[ 1- x- (1)/(3) (-2x+2)] } \, dx \\ \\ = \int\limits^1_0 { (3x)/(2)(-2x+2)^2[ 1- x+ (2x)/(3) - (2)/(3) ] } \, dx \\ \\ = \int\limits^1_0 { (3x)/(2)(-2x+2)^2[ (1)/(3) - (x)/(3)] } \, dx \\ \\ = \int\limits^1_0 { (3x)/(2)(-2x+2)^2( (1-x)/(3) ) } \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/a3whu1maxq9mgwq0wi7kyft6i97nxkftty.png)