SOLUTION
Given the question in the image, the following are the solution steps to answer the question.
STEP 1: Write the given data set
STEP 2: Find the finite difference
We first find the differences in the output values which is the population as seen below
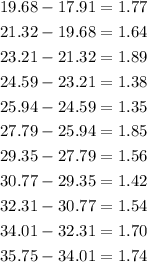
STEP 3: Find the second order difference
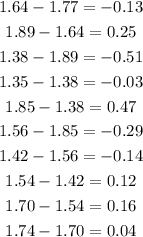
STEP 4: Find the third order difference
![undefined]()