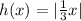An equation that represents a horizontal stretch by a factor of 3 of the graph of g(x)=|x| is
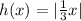 .
.
In Mathematics and Geometry, a function can be stretched by multiplying it with the absolute value of a numerical value that is either greater than 1 or less than -1. Additionally, you should multiply the x-variable with the shrink or stretch factor when compressing (shrinking) or stretching a function horizontally.
By critically observing the parent absolute value function g(x) = |x|, we can reasonably infer and logically deduce that it would be horizontally stretched by a stretch factor of 3.
In this context, an equation that represents a horizontal stretch by a factor of 3 of the graph of the parent absolute value function can be written as follows;
h(x) = g(1/3(x))