Answer:
The terminal velocities will be the same in a vacuum and different for the egg and further.
Step-by-step explanation:
Thinking process:
The terminal velocity is the maximum velocity that an object can attain after overcoming the resistance caused by the atmosphere or air. In other words, the velocity equation is given as:
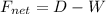
where F is the net force,
D = Drag force
W = Weight of the object falling down.
The drag force increases by the increase with the square of the velocity like this:
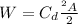
The terminal velocity is given by the equation:
V = Sqrt (2W/CdpA)
In the absence of friction, like a vacuum, the velocities are the same.
In the atmosphere, there is drag, and the velocities are different.