Answer:
For a: The mass of
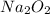 required is 23.4 grams
required is 23.4 grams
For b: The mass of NaOH required is 24 grams
For c: The mass of oxygen gas produced is 0.0984 grams.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
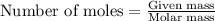 .....(2)
.....(2)
Given mass of oxygen gas = 4.80 g
Molar mass of oxygen gas = 32 g/mol
Putting values in equation 2, we get:
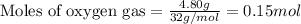
For the given chemical equation:
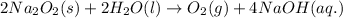
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of oxygen gas is produced from 2 moles of
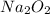
So, 0.15 moles of oxygen gas will be produced from =
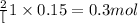 of
of
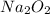
Now, calculating the mass of
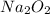 by using equation 1:
by using equation 1:
Molar mass of
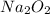 = 78 g/mol
= 78 g/mol
Moles of
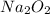 = 0.3 moles
= 0.3 moles
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
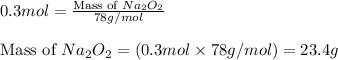
Hence, the mass of
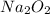 required is 23.4 grams
required is 23.4 grams
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
When 1 mole of oxygen gas is produced, then 4 moles of NaOH is also produced.
So, when 0.15 moles of oxygen gas will be produced, then =
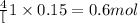 of NaOH will be produced.
of NaOH will be produced.
Now, calculating the mass of NaOH by using equation 1:
Molar mass of NaOH = 40 g/mol
Moles of NaOH = 0.6 moles
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
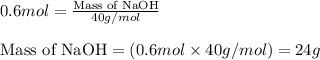
Hence, the mass of NaOH required is 24 grams
Given mass of
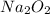 = 0.48 g
= 0.48 g
Molar mass of
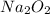 = 78 g/mol
= 78 g/mol
Putting values in equation 2, we get:
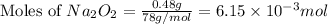
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
2 moles of
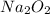 produces 1 mole of oxygen gas
produces 1 mole of oxygen gas
So,
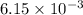 moles of
moles of
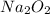 will produce =
will produce =
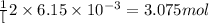 of oxygen gas
of oxygen gas
Now, calculating the mass of oxygen gas by using equation 1:
Molar mass of oxygen gas = 32 g/mol
Moles of oxygen gas =
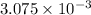 moles
moles
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
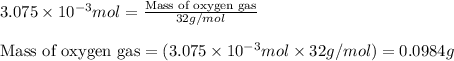
Hence, the mass of oxygen gas produced is 0.0984 grams.