For 1 mole of an ideal gas, we have PV=RT............(Eq. 1)
where, P = pressure
V= volume
R = universal gas constant
T = Temperature
Let, P1, V1 and T1 be initial pressure, volume and temperature of
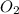
respectively
Let, P2, V2 and T2 be pressure, volume and temperature of
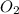
respectively, after application of pressure.
Using Eq. 1 we get,
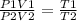
....... (Eq. 2)
Now, since that T1=T2 and P2=3(P1)
∴ Eq. 2 becomes P1V1=P2V2
∴
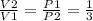
∴ V2 =
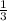
V1
Thus, final volume V2 will be 1/3 of initial volume V1