For a general reaction:
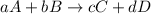
Expression for reaction quotient is written as follows:
![Q=([C]^(c)[D]^(d))/([A]^(a)[B]^(b))](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/tf0rvh22q10eu2yqvzxoa1e5yhz2gi894j.png)
Here, [A], [B], [C] and [D] is concentration of A, B, C and D respectively and a, b , c and d is their respective stoichiometry.
The given reaction is as follows:
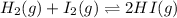
Thus, expression for reaction quotient will be:
![Q=([HI]^(2))/([H_(2)][I_(2)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/high-school/zttf64e4ysit1ijdrnrm4kkuqnkzuyluw8.png)
Putting the values,
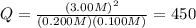
Therefore, the value of reaction quotient is 450.