A star forms when a molecular cloud collapses under its own gravity forming a dense core sustained by nuclear fusion. This happens only when the force of gravity pulling in exceeds the outward push of pressure. High-density molecular clouds have stronger forces of gravity pushing in, making it easier to overcome the total pressure within the cloud.
Once started, the collapse of the solar nebula continues because the force of gravity exerted on the cloud grows stronger as the cloud shrinks in size. The universal law of gravitation is written mathematically:
The force of gravity between two objects: F=GMM/d^2
Fg is the force of gravitational attraction, M1 and M2 are the masses of the two objects, and d is the distance between their centers. The symbol G is known as the gravitational constant. Its value is
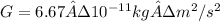 .
.
Before its collapse began, the gas that made up the solar nebula was probably spread out over a roughly spherical region a few light-years in diameter. This gas was extremely low in density and extremely cold.
Possible causes for the start of a collapse:
Shock wave from a nearby exploding star
Collision of 2 molecular clouds
So the two major forces in star is
1. Gravitation force between its core
2. Strong nuclear force between its nuclei.