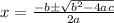Answer:
To complete the derivation of the quadratic equation:
Given:
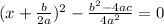
Add both sides
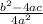 we have;
we have;
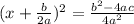
Taking square root both sides we have;
⇒
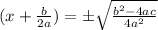
⇒
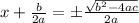
Subtract
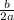 from both sides we have;
from both sides we have;
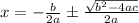
Therefore, complete derivation for the quadratic equation is:
Step 1.
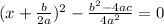
Step 2.
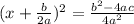
Step 3.
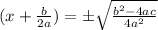
Step 4.
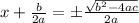
Step 5.
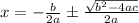
or