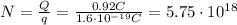The current is defined as the ratio between the charge Q flowing through a certain point of a wire and the time interval,
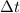
:
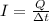
First we need to find the net charge flowing at a certain point of the wire in one second,
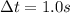
. Using I=0.92 A and re-arranging the previous equation, we find
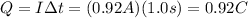
Now we know that each electron carries a charge of
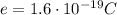
, so if we divide the charge Q flowing in the wire by the charge of one electron, we find the number of electron flowing in one second: