Answer:
1A. 20.5
2A. 14.54
1B. 14.625
2B. quite good reasonable
Explanation:
Mean is used to measure central tendency (i.e. representative of data) and standard deviation is use to measure dispersion of data. The formula use to calculate mean and variance is :
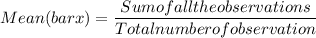
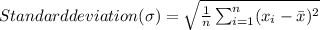
1A. Mean of six sample =
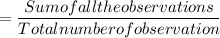
⇒
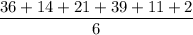
⇒ Mean = 20.5
Standard deviation of six sample =
![= \sqrt{(1)/(6)[ (36-20.5)^2+(14-20.5)^2+(21-20.5)^2+(39-20.5)^2+(11-20.5)^2+(2-20.5)^2}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/high-school/wraicc27msylqzfxfkb9rv5m0dw39w4l5c.png)
⇒ σ = 14.54
2A. Total number of error = 36 + 14 + 21 + 39 + 11 + 2 = 123
Total number of error made by all scans is 123 error per 6000 scans.
1B. Mean of all 12 samples is:
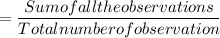
⇒
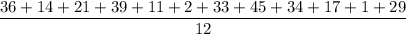
⇒ Mean = 23.5
Standard deviation of all 12 samples =
![= \sqrt{(1)/(12)[ (36-23.5)^2+(14-23.5)^2+(21-23.5)^2+(39-23.5)^2+(11-23.5)^2+(2-23.5)^2+(33-23.5)^2+(45-23.5)^2+(34-23.5)^2+(17-23.5)^2+(1-23.5)^2+(29-23.5)^2}]]()
⇒ σ = 14.625
2B. Taking small sample instead of large sample can be quite risky sometimes as larger sample give us more accurate result than small sample.
But here we can take a small sample because the mean of both the size of the sample is near about.