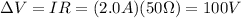We can solve the problem by using Ohm's law, which can be written as:
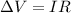
where
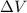
is the potential difference across the resistor
I is the current flowing in the circuit
R is the resistance
In our circuit, I=2.0 A and the resistance is
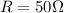
, so the potential difference across the batteries (equal to the potential difference of the battery) is