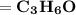Answer:
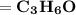
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information, since the molecular mass of the ion M+ is not given;
Let's assume M+ = 58.0423
So, by applying the 13th rule;
we will need to divide the mass by 13, after dividing it;
The quotient n = no. of carbon; &
The addition of the quotient (n) with the remainder r = no. of hydrogen.
So;
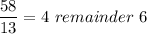
So;
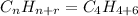
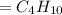
From the given information; we have oxygen present, so since the mass of oxygen = 16, we put oxygen in the molecular formula by removing
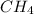 . Also, since the mass is an even number then Nitrogen is 0.
. Also, since the mass is an even number then Nitrogen is 0.
So, we have: