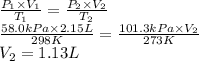Answer:
1.13 L
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data
- Initial pressure (P₁): 58.0 kPa
- Initial volume (V₁): 2.15 L
- Initial temperature (T₁): 25°C + 273.15 = 298 K
- Final pressure (P₂): 101.3 kPa
- Final temperature (T₂): 0°C + 273.15 = 273 K
We can find the final volume of the oxygen gas using the combined gas law.