Answer:
Universal Law of Gravitation
Step-by-step explanation:
Coulomb’s law explains the magnitude of force between two charges separated by a distance.
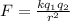
Universal Law of Gravitation. explains the magnitude of force between two masses separated by a distance.
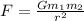
Newton’s second Law explains the relationship between force and acceleration
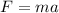
Snell’s Law explains the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction and the refractive indices of two refractive medium when light passes from one medium to another at a angle
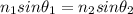
Law of Conservation of Energy explains how energy can neither be created nor be destroyed.
So Coulomb’s law , Universal Law of Gravitation and Newton’s second Law all give us the magnitude of force but only the columb's law and the universal law of gravitation are the Inverse Square Law.