Answer:
Specific heat of the unknown substance is 0.881 J/gC
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Mass of unknown substance, m(s) = 35.5 g
Initial temperature of the substance, T1 = 103 C
Mass of water, m(w) = 100 g
Initial temperature of water, T1 = 24 C
Final temperature of solution, T2 = 29.5 C
Formula:
Heat (q) absorbed or evolved by a substance is given as:
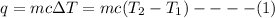
where, m = mass of the substance
c = specific heat
ΔT = change in temperature
Calculation:
Heat lost by the unknown substance = heat gained by water
Based on equation (1) we have:
Heat lost by the unknown substance = -m(s)*c(s)*ΔT
= -35.5*c*(29.5-103) = 2609.25c
heat gained by water = -m(w)*c(w)*ΔT=100*4.18*(29.5-24) =2299
Therefore,
2609.25c = 2299
c = 0.881 J/g C