Answer:-
![[H_3O^+]=4.2*10^-^1^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/x36q22iwg34jev6fwa3sg3jwybzhnyjeiy.png)
Solution:- Ammonia is a weak base. So, to calculate the hydroxide ion concentration we make the ice table:
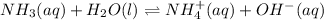
I 0.0032 0 0
C -X +X +X
E (0.0032-X) X X
![K_b=([NH_4^+][OH^-])/([NH_3])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/q03ymonat3t0fg1d2gkedvk4xmlvsoog06.png)
Kb value for ammonia is
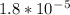 . Let's plug in the values and solve for X.
. Let's plug in the values and solve for X.
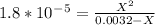
Kb value is very low so we can neglect the X on the bottom.
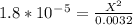
On cross multiply:
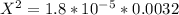
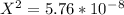
On taking square root:
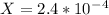
From ice table,
![[OH^-]]=X](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/884f4mi4xdbdnzu6kbvqkdb7gecsms0kjn.png)
So,
![[OH^-]=2.4*10^-^4](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/topitya0uhbb2iaf1alzzk8k6t12wkih58.png)
hydronium ion and hydroxide ion concentrations are related to each other by the formula:
![[H_3O^+][OH^-]=K_w](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/csl0njv5owhbubjafz95banafp22ac0i83.png)
where, Kw is the water dissociation constant and its value is
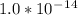
![[H_3O^+]=(1.0*10^-^1^4)/(2.4*10^-^4)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/i92i3dhagqomnyxw1xectxl7jw5nlbscoo.png)
![[H_3O^+]=4.2*10^-^1^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/x36q22iwg34jev6fwa3sg3jwybzhnyjeiy.png)