We can decompose the problem on x- and y-axis.
The position vector decomposed is:
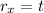
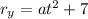
The velocity vector can be found computing the derivative of r on both axes:
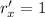
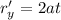
So, the velocity vector is
r' = 1
i+2at
j
The speed (the magnitude of the velocity vector) is
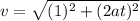
Finally we can write the acceleraion vector by performing derivation on the velocity vector:
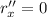
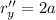
and so
r''=2a
j