We cause conservation of momentum. The initial momentum of the situation is zero, since momentum is given by p=mv. Initially v of the ball and man are zero so the total momenta (the sum of the ball's and man's momenta) is zero.
Conservation of momentum means the vector sum of the final momenta must equal zero. That is, they will be equal and opposite. When the ball goes forward at 15m/s the momentum is p=(4kg)x(15m/s)=60kgm/s.
The man must have the same momentum, but in the opposite direction (negative). We can find his speed by considering the magnitude of his velocity:
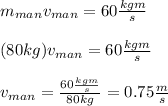
Checking our work we see that an 80kg man moving at 0.75m/s gives
(80kg)(0.75m/s)=60kgm/s, as expected.