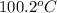Answer :
The freezing point of a solution is
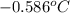
The boiling point of a solution is
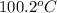
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the freezing point of solution.
Formula used :
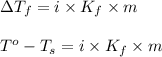
where,
 = change in freezing point
= change in freezing point
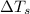 = freezing point of solution = ?
= freezing point of solution = ?
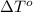 = freezing point of water =
= freezing point of water =
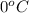
i = Van't Hoff factor = 3 (for K₂S electrolyte)
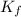 = freezing point constant for water =
= freezing point constant for water =
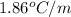
m = molality = 0.105 m
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get
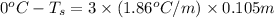
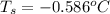
Thus, the freezing point of a solution is
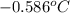
Now we have to calculate the boiling point of solution.
Formula used :
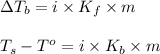
where,
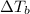 = change in boiling point
= change in boiling point
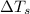 = boiling point of solution = ?
= boiling point of solution = ?
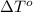 = boiling point of water =
= boiling point of water =
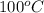
i = Van't Hoff factor = 3 (for K₂S electrolyte)
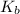 = boiling point constant for water =
= boiling point constant for water =
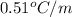
m = molality = 0.105 m
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get
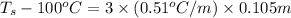
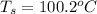
Thus, the boiling point of a solution is