Answer:
Congruent; Not Congruent; Congruent; Not Congruent; Not Congruent; Congruent
Explanation:
We will use the distance formula to find the length of each segment:
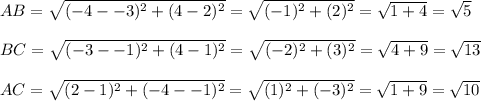
In order for ABC to be congruent to DEF, AB must be congruent to DE, BC must be congruent to EF, and AC must be congruent to DF:
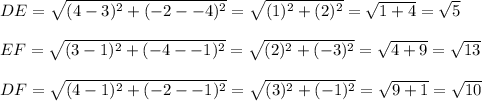
Since AB is congruent to DE, BC is congruent to EF and AC is congruent to DF, the two triangles are congruent.
In order for ABC to be congruent to JKL, AB must be congruent to JK, BC must be congruent to KL, and AC must be congruent to JL. We know the measurements of AB, BC and AC;
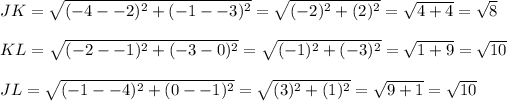
While AC is congruent to JL, the other two corresponding pairs of sides are not congruent. Therefore the triangles are not congruent.
In order for ABC to be congruent to QRS, AB must be congruent to QR, BC must be congruent to RS, and AC must be congruent to QS. We know the measurements of AB, BC and AC;
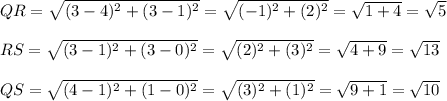
Since AB is congruent to QR, BC is congruent to RS, and AC is congruent to QS, this means that the two triangles are congruent.
Since ABC is congruent to DEF, and ABC is not congruent to JKL, this means that triangle DEF is not congruent to triangle JKL.
Since ABC is congruent to QRS, and QRS is not congruent to JKL, this means that triangle QRS is not congruent to JKL.
Since ABC is congruent to DEF and ABC is congruent to QRS, this means that DEF is congruent to QRS by the transitive property.