Answer: The kinetic energy of vase at 0.500 m position is 1.96 J
Step-by-step explanation:
Law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but it can only be transformed from one form to another form.
Here, the potential energy of the vase is getting converted into kinetic energy of the vase
So, calculating the potential energy of vase, we use the equation:
P = mgh
where,
m = mass of vase = 0.800 kg
g = acceleration due to gravity =
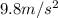
h = height of vase = (0.750 - 0.500) m = 0.250 m
Putting values in above equation, we get:
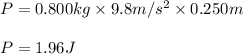
At 0.500 m, the potential energy gets converted to kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy of the vase = 1.96 J
Hence, the kinetic energy of vase at 0.500 m position is 1.96 J