Answer :
Part A : The balanced chemical equation is,
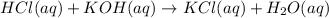
Part B : Molarity of Acid = 0.141 mole/L
Volume of Acid = 25 ml = 0.025 L
Molarity of Base = 0.0996 mole/L
Volume of Base = 35.38 ml = 0.03538 L
Part C : The number of moles of HCl = 0.003525 moles
Part D : The number of moles of NaOH = 0.003523 moles
Part E : The concentration of NaOH = 0.0996 mole/L
Solution : Given,
Molarity of Acid = 0.141 mole/L
Volume of Acid = 25 ml = 0.025 L
Volume of Base = 35.38 ml = 0.03538 L
Part A : The balanced chemical equation is,
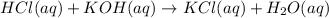
Part B : Acid = HCl Base = NaOH
Molarity of Acid = 0.141 mole/L
Volume of Acid = 25 ml = 0.025 L
Volume of Base = 35.38 ml = 0.03538 L
Now we have to calculate the Molarity of NaOH.
Formula used :
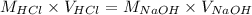
where,
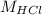 = Molarity of HCl
= Molarity of HCl
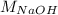 = Molarity of NaOH
= Molarity of NaOH
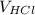 = Volume of HCl
= Volume of HCl
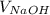 = Volume of NaOH
= Volume of NaOH
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get the value of
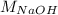 .
.
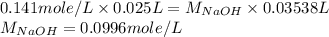
Therefore, The Molarity of Base (NaOH) = 0.0996 mole/L
Part C : we have to calculate the number of moles of HCl.
Formula used :
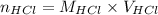
where,
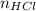 = Moles of HCl
= Moles of HCl
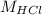 = Molarity of HCl
= Molarity of HCl
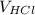 = Volume of HCl
= Volume of HCl
Now put the given values in above formula, we get
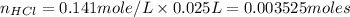
Therefore, the number of moles of HCl = 0.003525 moles
Part D : we have to calculate the number of moles of NaOH.
Formula used :
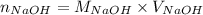
where,
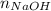 = Moles of NaOH
= Moles of NaOH
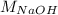 = Molarity of NaOH
= Molarity of NaOH
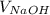 = Volume of NaOH
= Volume of NaOH
Now put the given values in above formula, we get
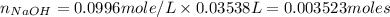
Therefore, the number of moles of NaOH = 0.003523 moles
Part E : we have to calculate the concentration of NaOH.
Formula used :
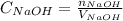
where,
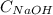 = Concentration of NaOH
= Concentration of NaOH
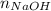 = Moles of NaOH
= Moles of NaOH
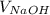 = Volume of NaOH
= Volume of NaOH
Now put the given values in above formula, we get
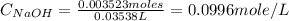
Therefore, the concentration of NaOH = 0.0996 mole/L