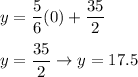We check the collinearity of points. If the points A(-15, 5), B(-9, 10) and C(-3, 15) are collinear, then the lines AB and BC are the same slope.
The formula of a slope:
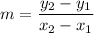
Substitute:
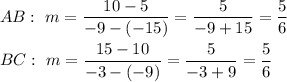
A, B and C are collinear.
The slope-point form:
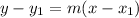
Substitute:

x-intercept: put y = 0 to the equation
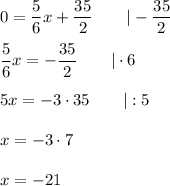
y-intercept: put x = 0 to the equation