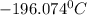The given linear equation is:
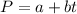
Determine the value of a and b (constants) by plug in the values of pressure and temperature.
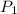 (Pressure of liquid nitrogen) =
(Pressure of liquid nitrogen) =
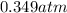
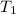 (Temperature of liquid nitrogen) =
(Temperature of liquid nitrogen) =
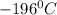
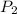 (Pressure of ethyl alcohol) =
(Pressure of ethyl alcohol) =
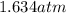
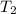 (Temperature of ethyl alcohol) =
(Temperature of ethyl alcohol) =
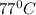
Put above values in given equation:
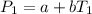
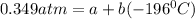 (1)
(1)
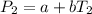
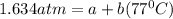 (2)
(2)
Subtract equation (1) from equation (2), we get the value of b
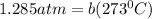
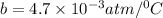
Now, put the value of b in equation (1)
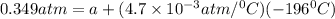
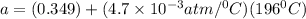
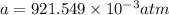
Now, at absolute zero, Pressure is equal to zero.
Absolute temperature =
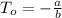
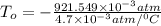
=
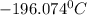
Thus, absolute zero =