Answer : The equilibrium constant kc is 4.76 x 10⁻³
Explanation :
The given equilibrium reaction is
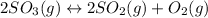
Step 1 : Set up ICE table
Let us set up an ICE table for this reaction .
The initial concentration of SO₃ is
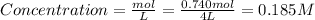
The initial concentrations of products are 0.
Let us assume x is the change .
Please refer the attached picture.
Step 2 : Use the given value to find x
From the ICE table, we can see that at equilibrium, concentration of O₂ is x
But we have been given that , at equilibrium we have 0.190 mol of O₂ .
Let us convert this to concentration unit.
Concentration of O₂ at equilibrium =
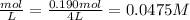
But concentration of O₂ from the ICE table is x.
Therefore we have x = 0.0475 M
Step 3 : Using x , find equilibrium concentrations
Using this value, let us write the equilibrium concentrations of the given species.
[SO₃]eq = 0.185 M - 2x = 0.185 - 2(0.0475) = 0.09 M
[SO₂]eq = 2x = 0.095 M
[O₂]eq = x = 0.0475 M
Step 4 : Set up equation for kc and solve it
The equilibrium constant kc is calculated as,
![k_(c) = ([SO_(2)]^(2) [O_(2)])/([SO_(3)]^(2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/opzhueaal9ytj4ui4nekd8ynxk4xe31oku.png)
Let us plug in the above equilibrium values.
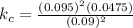
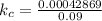
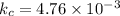
The equilibrium constant kc is 4.76 x 10⁻³