Hello!
We have the following data:
ps: we apply Ka in benzoic acid to the solution.
[acid] = 0.235 M (mol/L)
[salt] = 0.130 M (mol/L)
pKa (acetic acid buffer) =?
pH of a buffer =?
Let us first find pKa of benzoic acid, knowing that Ka (benzoic acid) =

So:
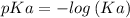
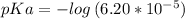
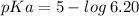
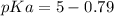
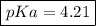
Now, using the abovementioned data for the pH formula of a buffer solution or (Henderson-Hasselbalch equation), we have:
![pH = pKa + log\:([salt])/([acid])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/cghtr35x7z5a8th8q5gvuwazwsd9awuklk.png)
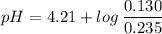
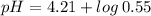
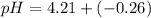
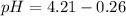

Note:. The pH <7, then we have an acidic solution.
I Hope this helps, greetings ... DexteR! =)