Answer:- The Ka for the acid is
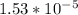 .
.
Solution:- In general, monoprotic acid could be represented by HA. The dissociation equation for the ionization of HA is written as:
HA(aq)\rightarrow H^+(aq) + A^-(aq)
Now, we make the ice table for this equation as:
HA(aq)\rightarrow H^+(aq) + A^-(aq)
I 0.25 0 0
C -X +X +X
E (0.25 - X) X X
where, I stands for initial concentration, C stands for change in concentration and E stands for equilibrium concentration.
X is the change in concentration and from ice table it's same as the concentration of hydrogen ion that is calculated from given pH.
![Ka = [H^+][A^-](1)/(HA)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/szi4bdnkk4q3pwj3gluyqjqmyfogm9om0v.png)
Where, Ka is the acid ionization constant. Let's plug in the values.
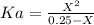
Let's calculate the value of X first using the equation:
![pH = -log[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/i4vjb5ntyivyh69bjfz0gm3pquch6xsr8l.png) [/tex]
[/tex]
on taking antilog ob above equation we get:
![[H^+]=10^-^p^H](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/xlwyy2m2aht3l7rpiyt0ewfo587ulpmrdf.png)
![[H^+]=10^-^2^.^7^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/n54oliy46plu97lz31vd64w4wytq7i2hv7.png)
![[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/cky1neqovqbkiy0bd9cgh9ska0qfqez5o0.png) = 0.00195
= 0.00195
So, X = 0.001195
Let's plug in this value of X in the equation:-
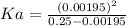
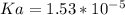
So, the value of Ka for butyric acid is
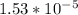 .
.