Answer:
For 1: The oxidation state of Mn is +4 and oxidation state of O is -2.
For 2: The oxidizing agent is
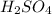 and reducing agent is HBr.
and reducing agent is HBr.
Step-by-step explanation:
The oxidation state of oxygen is taken to be -2. To calculate the oxidation state of manganese, in a neutral manganese oxide compound, we take the oxidation state of manganese be 'x'.

Hence, the oxidation state of Mn is +4 and oxidation state of O is -2.
Oxidizing agent is defined as the reagent which helps the other substance to get oxidized and itself gets reduced. The oxidation state gets reduced.
Reducing agent is defined as the reagent which helps the other substance to get reduced and itself gets oxidized. The oxidation state is increased.
In the given chemical equation:

On the reactant side:
Oxidation state of hydrogen = +1
Oxidation state of bromine = -1
Oxidation state of sulfur = +6
Oxidation state of oxygen = -2
On product side:
Oxidation state of hydrogen = +1
Oxidation state of bromine = 0
Oxidation state of sulfur = +4
Oxidation state of oxygen = -2
As, the oxidation state of sulfur is decreasing, it is undergoing a reduction reaction and hence is an oxidizing agent. And, the oxidation state of bromine is increasing, it is undergoing an oxidation reaction and hence is an reducing agent.