For this case we have the following inequality:
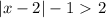
We can rewrite the inequality as follows:
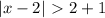
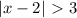
From here, we have two possible cases:
Case 1:
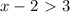
Case 2:

Therefore, graphically, it is observed that the solution is:
(5, ∞)
(-∞, -1)
To do this, we must observe the shaded region in the graph, or equivalently the numerical line.
Answer:
(5, ∞)
(-∞, -1)
See attached image for the graphic solution